How Brain Anatomy Affects Everything You Do: Insights from Cortex Curious
The human brain is an extraordinary organ, controlling every action, thought, and feeling you experience. When you stop to think about it, it’s almost miraculous how this single, complex structure orchestrates everything from simple movements to deep, philosophical musings. The brain doesn’t just manage basic functions like breathing or walking—it also governs emotions, memory, creativity, and even your sense of self. Understanding brain anatomy and how it affects what you do can open up a world of fascinating insights into human behavior, cognition, and health.
This article delves into the role of brain anatomy in shaping your actions and experiences. By exploring the brain’s various parts and functions, you can gain a deeper understanding of how physical changes in the brain influence everything from learning and decision-making to mood regulation and motor skills. Whether you’re looking to improve cognitive performance, better understand your emotional responses, or simply curious about the science behind everyday actions, this exploration of brain anatomy will give you a new perspective on why you do what you do.
The Structure of the Brain: A Quick Overview
Before diving into the specifics of how brain anatomy affects behavior, it’s important to have a basic understanding of its structure. The human brain consists of several key parts, each with its own specialized function. At the highest level, the brain can be divided into the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
- The Cerebrum: This is the largest part of the brain, responsible for higher functions such as reasoning, memory, and voluntary movements. It is divided into two hemispheres (left and right), each responsible for different tasks. For instance, the left hemisphere is often linked to logic and language, while the right hemisphere is more involved with creativity and spatial awareness.
- The Cerebellum: Found at the back of the brain, the cerebellum controls coordination, balance, and fine motor skills. It plays an essential role in movements like walking, typing, and even maintaining posture.
- The Brainstem: Connecting the brain to the spinal cord, the brainstem controls fundamental life functions like heartbeat, breathing, and digestion. It serves as the brain’s basic control center for survival.
Each of these parts works in harmony to ensure that your brain can carry out a vast array of tasks, from breathing without conscious thought to making complex decisions.
The Role of Brain Anatomy in Behavior and Cognition
Brain Anatomy plays a vital role in how we think, feel, and act on a daily basis. Different areas of the brain contribute to various cognitive functions, emotions, and behaviors. For example:
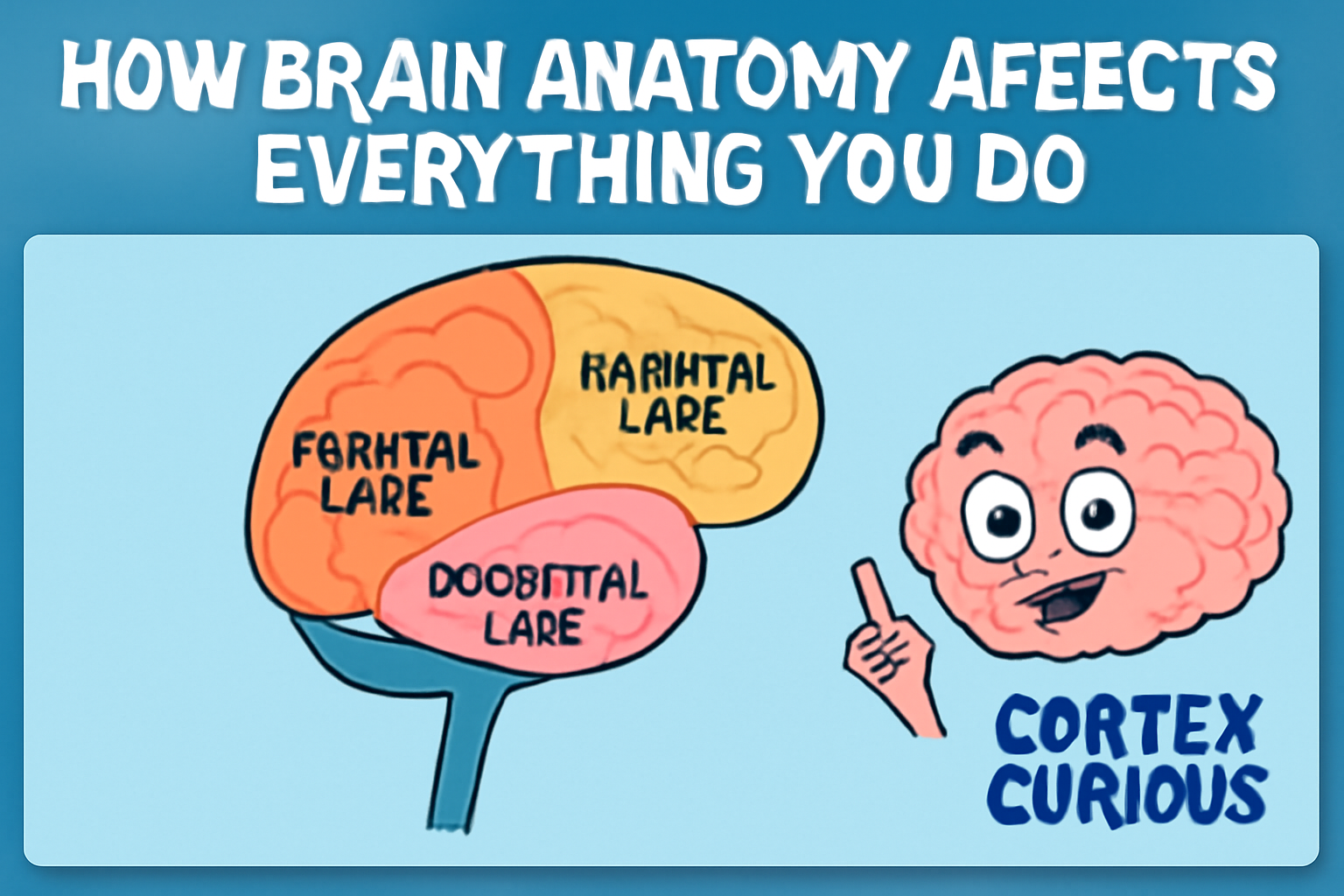
- The Frontal Lobe: Often referred to as the brain’s control center, the frontal lobe governs reasoning, problem-solving, judgment, and planning. It also plays a key role in regulating emotions and social behavior. Damage to the frontal lobe can lead to personality changes, impulsive behavior, and difficulty with decision-making.
- The Parietal Lobe: This area of the brain is involved in processing sensory information, such as touch, temperature, and pain. It also helps with spatial orientation and coordination. People with damage to the parietal lobe may experience difficulty with tasks like reading, writing, or even navigating familiar environments.
- The Temporal Lobe: Responsible for processing auditory information and memory, the temporal lobe plays a key role in language comprehension and emotion. Damage to this region can result in memory loss, difficulty understanding speech, or changes in emotional responses.
- The Occipital Lobe: The occipital lobe is primarily concerned with visual processing. It helps you recognize shapes, colors, and motion. Visual processing issues arising from damage to this area can lead to difficulty recognizing faces or objects, even though a person may still have intact eyesight.
Understanding how these different regions of the brain function and interact with each other can shed light on why you act and react the way you do in different situations. The physical structure of your brain directly impacts your ability to process information, manage emotions, and carry out everyday tasks.
How Brain Anatomy Influences Memory and Learning
One of the most fascinating aspects of brain anatomy is its role in memory and learning. The brain is incredibly adept at storing and retrieving information, thanks to specialized regions such as the hippocampus and amygdala. The hippocampus is responsible for forming new memories, while the amygdala plays a significant role in emotional memory and responses. These two structures work closely together to help you retain important information, while also linking it to your emotional experiences.
When you learn something new, the brain creates new connections between neurons—this process is called neuroplasticity. Over time, these connections strengthen, making it easier to recall information or perform a skill. However, brain anatomy can influence the effectiveness of this process. For example, individuals with damage to the hippocampus may have difficulty forming new memories or recalling past experiences. On the other hand, people with an intact hippocampus tend to have better recall and learning abilities.
Interestingly, brain anatomy also plays a role in how you learn. Research has shown that people with stronger connections between different brain regions tend to perform better on cognitive tasks. This underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy brain through activities that challenge and stimulate cognitive function, such as learning new skills, reading, or engaging in complex problem-solving exercises.
The Brain and Emotional Regulation
Emotions are deeply rooted in brain anatomy, particularly in regions like the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. The amygdala is responsible for processing emotional stimuli, such as fear, anger, and pleasure, while the prefrontal cortex helps regulate these emotions and allows you to control your responses.
For example, when you face a stressful situation, your amygdala activates the body’s “fight or flight” response. This leads to the release of hormones like adrenaline, preparing you for action. However, it is the prefrontal cortex that helps you assess the situation and decide whether to react calmly or impulsively. In some cases, damage to the prefrontal cortex can impair emotional regulation, leading to difficulty managing stress or anger.
The balance between these two brain regions is critical for emotional stability. When the amygdala is overactive and the prefrontal cortex is underactive, individuals may experience heightened emotional responses, such as anxiety or aggression. On the other hand, when the prefrontal cortex is functioning optimally, it can help moderate intense emotions and foster a more balanced emotional state.
Motor Skills and Brain Anatomy
From simple tasks like brushing your teeth to more complex activities like playing the piano, motor skills are a fundamental part of your daily life. These skills are largely controlled by the motor cortex, a region in the frontal lobe. The motor cortex sends signals to the muscles, enabling them to perform precise movements.
The cerebellum also plays a key role in motor coordination. It helps fine-tune movements by processing feedback from the body and adjusting the signals sent by the motor cortex. This is why the cerebellum is so important for activities that require precision, such as typing, playing sports, or even walking without stumbling.
Interestingly, the brain’s ability to control motor skills improves with practice. As you repeat a movement or task, neural pathways become more efficient, making the action smoother and more automatic. However, damage to the motor cortex or cerebellum can lead to motor impairments, such as difficulty walking or executing complex movements.
Brain Anatomy and Decision Making
Decision-making is one of the most critical cognitive functions that brain anatomy influences. The prefrontal cortex, as mentioned earlier, is at the heart of decision-making. This area helps you weigh pros and cons, consider long-term consequences, and make informed choices.
When the prefrontal cortex is working well, you can make rational, well-thought-out decisions. However, when this region is impaired—whether due to injury, stress, or neurological conditions—individuals may struggle with impulsive behavior or poor decision-making. This is why emotional and psychological well-being plays such an important role in our ability to make sound choices.
The Influence of Brain Anatomy on Personality
Your personality, the set of characteristics that define who you are, is also shaped by brain anatomy. The prefrontal cortex, in particular, plays a large role in regulating personality traits such as self-control, empathy, and social behavior. For example, individuals with a well-functioning prefrontal cortex are more likely to exhibit behaviors like self-restraint and consideration for others.
Moreover, studies have shown that certain brain regions are associated with particular personality traits. For example, the medial prefrontal cortex is linked to self-reflection and introspection, while the ventromedial prefrontal cortex is involved in processing rewards and making choices that align with your values. Understanding how these areas work can provide insights into why we behave the way we do in different situations.
Conclusion
Brain anatomy is an incredibly powerful force in shaping every aspect of your life. From the way you think and learn to how you feel and act, the structure of your brain plays a role in everything you do. By understanding the various regions of the brain and their functions, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human behavior and cognition. Whether you’re striving to improve your cognitive performance, regulate your emotions, or better understand your actions, knowledge of brain anatomy is a valuable tool for self-awareness and personal growth.
For more insights into the incredible complexity of the brain, explore more at https://cortexcurious.com.



